An Electronic Medical Record (EMR) is a digital version of the traditional paper-based medical record for an individual. The EMR represents a medical record within a single facility, such as a doctor’s office or a clinic. Are you also looking to implement EMR technology into your practice? If so, then this blog will be a perfect guide and help you implement the best possible solution.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is an Electronic Medical Record?
EMR is an abbreviation for electronic medical records. Electronic medical records are more than just an alternative to paper medical records. They allow for a better coordination between healthcare professionals and departments, which helps provide the best possible service.
When you read a person’s electronic medical records, you can find information about that person’s treatment data and medical history. These records are collected by the patient’s doctor. Automated Medical Records keep track of all their past treatments and diagnosis.
In the modern world, EMR technology are becoming standard. In fact, they’re slowly but surely becoming a part of a new government requirement that is centered around the safe collection, storage and access of patients’ medical data.
An EMR includes information about a specific patient, including:
- Patient contact information, including emergency contact(s)
- Vitals, such as height, weight, body mass index (BMI) and body temperature
- Past and future medical facility appointments
- Physician orders
- Prescriptions
- Medical progress and surgical notes
- Consent to release information forms
- Allergies
- Past medical history
- Billing information, such as insurance
- Discharge summaries and treatment plans
There are two key pieces to this definition:
- EMR software helps to manage the creation, organization, and retrieval of electronic patient records.
- EMR software does not enable you to share electronic records with other organizations (unlike electronic health records, or EHR, software.
A typical EMR solution allows Physicians and Clinicians to easily manage
- Patient Charts: Create patient charts electronically at the point of care that include demographics, clinical health histories, allergy information, medications, immunization records, progress notes, lab results, and more
- ePrescriptions: Generate and send prescriptions to pharmacies electronically
- Lab Orders: Electronically create and send orders for lab work, medical tests, and consultations
- Billing: Capture all evaluation and management codes at the point of care to ensure complete invoices and eliminate down coding.
EMR Technology Basic Features
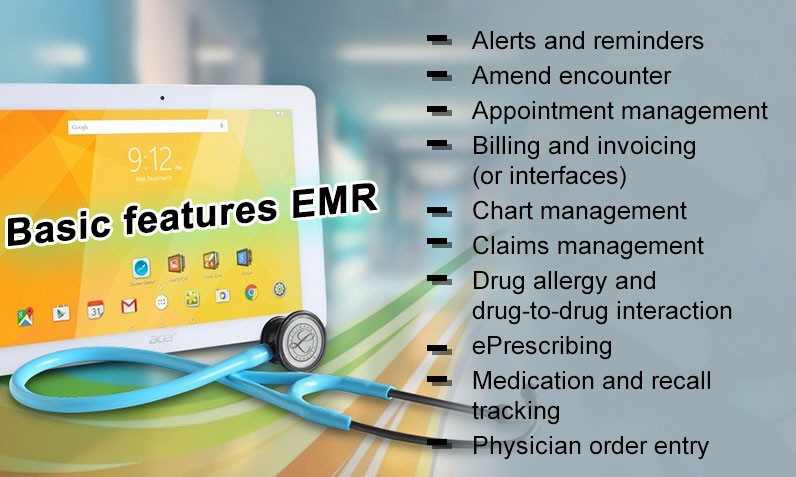
- Alerts and reminders
- Amend encounter
- Appointment management
- Billing and invoicing (or interfaces)
- Chart management
- Claims management
- Drug allergy and drug-to-drug interaction
- ePrescribing
- Medication and recall tracking
- Physician order entry
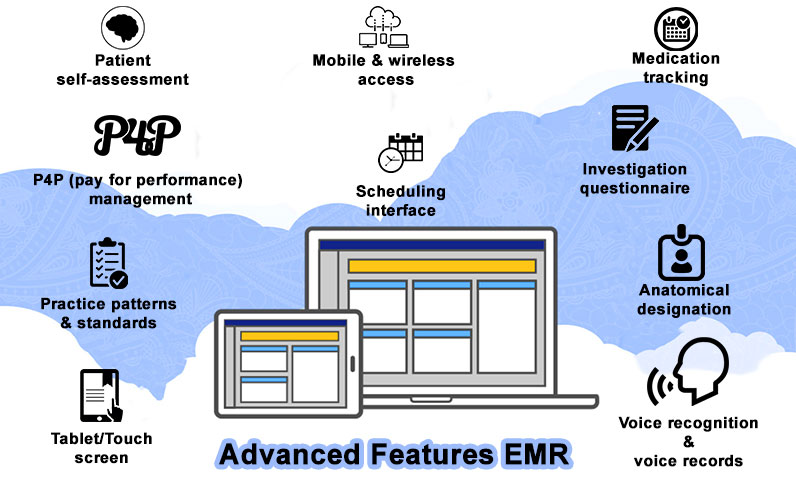
EMR Technology Advanced Features
- Anatomical designation
- Investigation questionnaire
- Medication tracking
- Mobile and wireless access
- Patient self-assessment
- P4P (pay for performance) management
- Practice patterns and standards
- Scheduling interface
- Tablet/Touch screen
- Voice recognition and voice records
Other Features That May be Included in An EMR Solution
- Clinical care and decision support
- Clinical flow sheets
- Clinical pathways integration
- Document scanning and management
- HL7 lab interface
- Patient portal and education
- Prescription drug database
- Template management
The Advantages of an EMR
Benefits of EMRs for Patients
- Fewer errors on medical records
- Quicker assessment and care from medical professionals
- Data and results are tracked over time
- Improved health diagnosis, treatment and overall quality of care
- Identify patients who are due for preventive visits and screenings
- Enhanced privacy and security of patient data
- Reduction in patient errors and improved patient care
- Enable evidence-based decisions at point of care
- Follow-up information after a visit such as self-care instructions, reminders for other follow-up care, and links to web resources
- Access to patient’s own records to view medications and keep up with lifestyle changes that have improved their health.
Benefits of EMRs for Clinics
- Save space by eliminating paper records needing to be stored, managed and retrieved
- Optimize workflow and increased number of patients served per day
- Reduce administrative difficulties and operational costs
- Interface easily with hospitals, pharmacies, labs and state health systems
- Customizable and scalable electronic records
- Gather and analyze patient data that enables outreach to discreet populations
- Provide clinical alerts and reminders
- Improve documentation and coding
- Enhance research and monitoring for improvements in clinical quality
- Provide built-in safeguards against prescribing treatments that would result in adverse events
- Track electronic messages to staff, other clinicians, hospitals, labs, etc.
- Links to public health systems such as registries and communicable disease databases
Why is EMR Technology Important for Healthcare Industry?
EMR Technology offers a range of benefits to physicians as well as the technology industry. Healthcare professionals would have to adapt if they weren’t used as broadly in practice.
Electronic medical records are a new & exciting development in healthcare. With these, hospitals can easily save loads of space with virtual records that don’t need to be stored in the building. In this modern world, the population is constantly growing and each doctor will gradually have more patients. – As the number of patients grows, so will the number of patient records. Providing more storage space may not be financially feasible for smaller clinics.
Using electronic medical records can potentially save a huge amount of time. This is because the records can be accessed quickly, for example by tapping on a file on a device. EMRs are sometimes hosted on different computers and can be stored on secure servers, which can make it difficult for healthcare professionals to find specific records. These types of systems are designed to be easy for the user so that they don’t have difficulty in finding files like x-rays or lab results. Online, EMR’s are organised and stored for easy access. All a doctor has to do is enter a name or date of birth, and the information is found in seconds
What Is EMR Software Development Cost?
We can assist! Get the FREE estimation of your product idea.
Contact UsFAQs
Q1. What are the 3 types of health records?
Health records can be classified as Electronic health records (EHRs), electronic medical records (EMRs), and personal health records (PHRs).
Q2. What is the difference between EMR and EHR?
EMRs are digital copies of patient medical history and treatment. EHRs, on the other hand, offer a detailed view of a patient’s health across multiple providers and healthcare organizations.
Q3. What is the difference between EMR and EHRs in terms of HIPAA?
Both systems must comply with HIPAA regulations for patient privacy and security. But EHRs have more advanced security features because they share information across multiple providers and organizations.
Q4. What information does an EMR store?
An EMR has the patient’s basic information, medical history, diagnoses, medications, allergies, lab results, radiology images, and treatment plans.
Q5. Do hospitals use EHR or EMR Technology?
Most hospitals use EHRs. They are more in-depth and detailed- as they store information across multiple providers and healthcare organizations.
Q6. What is the best EMR for a small/medium practice?
The best EMR for a particular practice will depend on the specific needs and requirements. Contact the VcDoctor team and get a free quote today.
.










